Archive
Silver Eagles Soar
Submitted by: Richard (Rick) Mills | Ahead of the Herd
-
As a general rule, the most successful man in life is the man who has the best information
In World War I severe material shortages played havoc with production schedules and caused lengthy delays in implementing programs. This led to development of the Harbord List – a list of 42 materials deemed critical to the military.
After World War II the United States created the National Defense Stockpile (NDS) to acquire and store critical strategic materials for national defense purposes. The Defense Logistics Agency Strategic Materials (DLA Strategic Materials) oversees operations of the NDS and their primary mission is to “protect the nation against a dangerous and costly dependence upon foreign sources of supply for critical materials in times of national emergency.”
The NDS was intended for all essential civilian and military uses in times of emergencies. In 1992, Congress directed that the bulk of these stored commodities be sold. Revenues from the sales went to the Treasury General Fund and a variety of defense programs - the Foreign Military Sales program, military personnel benefits, and the buyback of broadband frequencies for military use.
American Silver Eagle
The American Silver Eagle is the official silver bullion coin of the United States. It was first released by the United States Mint on November 24, 1986 and is struck only in the one troy ounce size.
 The Bullion American Silver Eagle sales program ultimately came about because the US government wanted, during the 1970s and early 1980s, to sell off what it considered excess silver from the Defense National Stockpile.
The Bullion American Silver Eagle sales program ultimately came about because the US government wanted, during the 1970s and early 1980s, to sell off what it considered excess silver from the Defense National Stockpile.
“Several administrations had sought unsuccessfully to sell silver from the stockpile, arguing that domestic production of silver far exceeds strategic needs. But mining-state interests had opposed any sale, as had pro-military legislators who wanted assurances that the proceeds would be used to buy materials more urgently needed for the stockpile rather than merely to reduce the federal deficit.” Wall Street Journal
The authorizing legislation for the American Silver Eagle bullion sales program required that the silver used for the coins had to be from the Defense National Stockpile. By 2002 the DNS stockpile was so depleted of silver that if the American Silver Eagle bullion sales program was to continue further legislation was required.
On June 6, 2002, Senator Harry Reid (D-Nevada) introduced the Support of American Eagle Silver Bullion Program Act to “authorize the Secretary of the Treasury to purchase silver on the open market when the silver stockpile is depleted.”
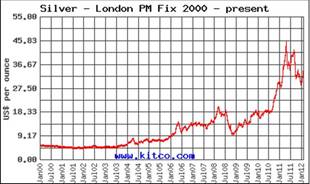
2002 - 10,539,026 Bullion American Silver Eagles were sold.
2003 - 8,495,008 Bullion American Silver Eagles were sold, silver averaged $4.88 an ounce for the year.
2004 - 8,882,754 Bullion American Silver Eagles were sold. For 2004 the average cost of an ounce of silver was $6.67.
2005 - 8,891,025 Bullion American Silver Eagles were sold. Silver averaged $7.32 an ounce.
2006 - 10,676,522 Bullion American Silver Eagles were sold. Silver averaged $11.55 an ounce
2007 - 9,028,036 Bullion American Silver Eagles were sold.
2008 - 20,583,000 Bullion American Silver Eagles were sold. Silver averaged $14.99 an ounce and almost 80% more Bullion American Silver Eagles were sold then in any previous year.
The US Mint suspended sales of the silver bullion coins to its network of authorized purchasers twice during the year.
In March 2008, sales increased nine times over the month before - 200,000 to 1,855,000.
In April 2008, the United States Mint had to start an allocation program, effectively rationing Silver Eagle bullion coins to authorized dealers on a weekly basis due to “unprecedented demand.”
On June 6, 2008, the Mint announced that all incoming silver planchets were being used to produce only bullion issues of the Silver Eagle and not proof or uncirculated collectible issues.
The 2008 Proof Silver Eagle became unavailable for purchase from the United States Mint in August 2008.
2009 - 30,459,000 Bullion American Silver Eagles were sold
On March 5, 2009, the United States Mint announced that the proof and uncirculated versions of the Silver Eagle coin for that year were temporarily suspended due to continuing high demand for the bullion version.
On October 6, 2009, the Mint announced that the collectible versions of the Silver Eagle coin would not be produced for 2009.
The sale of 2009 Silver Eagle bullion coins was suspended from November 24 to December 6 and the allocation program was re-instituted on December 7.
Silver Eagle bullion coins sold out on January 12, 2010.
The average cost of an ounce of silver in 2009 was $14.67
2010
No proof Silver Eagles were released through the first ten months of the year, and there was a complete cancellation of the uncirculated Silver Eagles.
Production of the 2010 Silver Eagle bullion coins began in January instead of December as usual. The coins were distributed to authorized dealers under an allocation program until September 3.
In 2010 the US Mint sold 34,700,000 Bullion American Silver Eagle Coins.
2011
According to the USGS’s most recent Silver Mineral Industry Survey, silver production fell to 37 tonnes in October - compared to 53 tonnes year over year (yoy).
In 2011, the United States produced approximately 1,054 tonnes of silver – down from 2010’s production of 1,154 tonnes and down from 2007’s production of 1,163 tonnes.
 The US imported 6,600,000 oz of silver for consumption in 2011 – up from 2007’s imports of 4,830,000 oz.
The US imported 6,600,000 oz of silver for consumption in 2011 – up from 2007’s imports of 4,830,000 oz.
In 2011 the US Mint sold 39,868,500 Bullion American Silver Eagle Coins.
2011 was the first year in which official coin sales will surpass domestic silver production.
Jeff Clark of Casey Research writes“For the first time in history, sales of silver Eagle and Maple Leaf coins surpassed domestic production in both the US and Canada. Throw in the fact that by most estimates less than 5% of the US population owns any gold or silver and you can see how precarious the situation is. A supply squeeze is not out of the question – rather it is coming to look more and more likely with each passing month.”
The US Mint is required by law to mint the bullion Silver Eagles to meet public demand for precious metal coins as an investment option. The numismatic versions of the coin (proof and uncirculated) were added by the Mint solely for collectors.
2012
United States Mint Authorized Purchasers (AP’s) ordered 3,197,000 Bullion American Silver Eagle Coins on January 3rd, the first day they went on sale. That opening day total catapulted January Bullion Eagle sales higher than half of the monthly totals in 2011.
As of January 25th 2012, 5,547,000 Bullion American Silver Eagle Coins had been sold.
Bullion Silver Eagles are guaranteed for weight and purity by the government of the United States and because of this the US government allows bullion Silver Eagles to be added to Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs).
Conclusion
The twin policies of zero interest rates and the continual creation of money and credit being enacted today, by all governments and central banks, means that the purchase of precious metals is the only way to protect the value of your assets.
“Mark my words, if the interest rates on U.S. government debt truly reflected both the real level of inflation in this country and the rising risk of some form of default, rates would already by sky-high and the U.S. would resemble a massive Greece.” John Embry, Chief Investment Strategist, Sprott Asset Management
Investors are currently risk adverse and mining stocks are not well understood by the general investing public, but at least one thing is going to become very apparent to most - the best way to hedge yourself against inflation could be owning silver.
Junior resource companies offer the greatest leverage to increasing demand and rising prices for silver. Junior resource companies are soon going to have their turn under the investment spotlight and should be on every investors radar screen. Are they on yours?
If not, maybe they should be.
Richard (Rick) Mills
[email protected]
www.aheadoftheherd.com
The Greatest Risk for Gold Investors
By Jeff Clark | BIG GOLD
While we’re convinced that our gold and silver investments will pay off, they don’t come without risk. What do you suppose is the biggest risk we face? Another 2008-style selloff? Gold stocks never breaking out of their funk? Maybe a depression that slams our standard of living?
Though those things are possible, we at Casey Research don’t see that as your greatest threat:
“Your biggest risk is not that gold or silver may fall in price. Nor is it that gold stocks could take longer to catch fire than we think. Not even the prospect of the Greater Depression. No, your biggest risk is political. As bankrupt governments get increasingly desperate for revenue, any monetary asset held domestically could be a target. It is absolutely essential that every investor diversify themselves politically. In fact, at this point, it is the one action that should be taken before anything else.” - Doug Casey, September 2011
I know many reading this are prudent investors. You own gold and silver as solid protection against currency debasement, inflation, and faltering economies. You set aside cash for emergencies. You have strong exposure to gold stocks, both producers and juniors, positioned ahead of what is likely the next-favored asset class. You feel protected and poised to profit.
Yet, despite all this preparation, you remain exposed to one of the biggest risks.
Similar to holding a diversified portfolio at a bank without checking the institution‘s solvency, many investors keep their entire stash of precious metals inside one political system without considering the potential trap they‘ve set for themselves. While storing some of your gold outside your home country is not a panacea, it does offer one important thing: another layer of protection.
Consider the exposure of the typical US investor:
- systemic risk, because both the bank and broker are US domiciled
- currency risk, as virtually every transaction is made in US dollars
- political risk, because they are left totally exposed to the whims of a single government
- economic risk, by being vulnerable to the breakdown of a single economy
Viewed in this context, the average US investor has minimal diversification.
The remedy is to internationalize the storage of some of your precious metals. This act reduces four primary risks:
Confiscation: We don‘t know the likelihood of another gold confiscation. But we do know that things are working against us - particularly for US citizens. With $14.7 trillion of debt and $115 trillion of unfunded liabilities, the US government will likely pursue heavy-handed solutions. Under the 1933 FDR “gold confiscation” in the US (the executive order was actually a forced delivery of citizens‘gold in exchange for cash), foreign-held gold was exempted.
Capital Controls: Many Casey editors think some form of capital controls lie ahead, limiting or eliminating a citizen‘s ability to carry or send money abroad. If enacted, all your capital would be trapped inside the US and at the mercy of whatever taxing and regulating schemes the government might concoct. Although you might be able to leave the country, your assets could not travel with you.
Administrative Action: There are plenty of horror stories of asset seizure by a government agency without any notice or due process, possibly leaving the victim without the means to mount a legal defense. Having some gold or silver stored elsewhere provides what could be your only available source of funds in such a scenario.
Lack of Personal Control: Having gold and silver stored elsewhere adds to your options. You will have a source of funds available for business, entrepreneurial pursuits, investment, or pleasure.
Foreign-held assets also require greater awareness and planning:Notice above we said these risks can be reduced, not eliminated. There is no perfect solution; US persons could, for example, be compelled to pay a “wealth tax” on assets held worldwide, or even repatriate them in a worst-case scenario. Absent a crystal ball, the political diversity of asset location is an essential strategy against an uncertain future.
- Access to your metal or sale proceeds may not be quick. Therefore, this option is for those with some gold and silver stored at or near home. We do not recommend storing all your precious metals overseas; that defeats one of its purposes, to have it handy for an emergency.
- While we think the US poses the greatest threat, a foreign government could move to control certain assets as well. The risk varies by country and is generally greater within the banking system than with private vaulting facilities.
- Understanding and complying with reporting requirements is essential.
The bottom line, though, is that foreign-held precious metals can mitigate risk and give you more options. And as your metal holdings grows, diversification becomes more crucial.
Given our current rapacious climate, it‘s likely that simply buying gold won‘t be enough. We strongly suggest every investor diversify one‘s bullion storage outside their current political regime. The option may not be available someday, leaving you vulnerable without a secondary source of bullion.
We advise taking advantage of the opportunity before it is gone.
[One way to internationalize your bullion is to use a safe deposit box in a second country; however, this requires traveling to the institution to handle the paperwork and organizing the transport of your bullion... and the contents of a safe deposit box aren't insured. Other programs will store gold; but the metal is often held in the form of fractional ownership in a 400-oz. bar and not specific coins and bars held in your name. A better solution is to store your bullion in a non-bank depository, outside your home country, without shared ownership, and do it for a reasonable fee. We found a program that provides all those things; and it offers BIG GOLD readers six months' free gold and silver storage in a Canadian vault. A risk-free, three-month trial subscription to BIG GOLD will qualify you for that deal... plus all the expert analysis and actionable investment advice packed into each issue.]
Related Articles:
Suicide of the Saver
Submitted by Adrian Ash | BullionVault
-
Savers and pensioners! Your murderers need no revolution to storm your stately homes…
SO IT’S NOW 100 years since Great Britain established its welfare state, writes Adrian Ash online gold market BullionVault.
Shortly after, and as the First World War kicked off, Britain then abandoned the free exchange of bullion for notes under the classical Gold Standard. Those 3 events were a long way from simple coincidence, of course. But 100 years later, it is the monetary revolution which feels most pressing today.
Political fighting over the welfare state is hotting up, but a European shooting match looks unlikely (for now). Whereas UK savers and retirees risk getting slaughtered, alongside their peers on the continent, across North America and pretty much everywhere else.
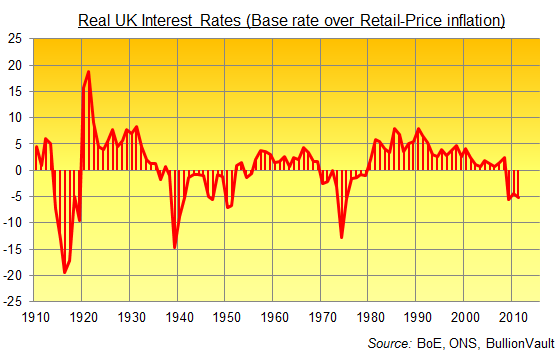
Compared to the previous 100 years, real UK interest rates – the returns paid to cash deposits over and above inflation – have been atrocious since 1911. Averaging less than 0.9% per year, they’ve been a fraction of the 4.4% averaged in the 100 years starting in 1811, just after the British Parliament’s Bullion Committee recommended a full return to gold following the Napoleonic Wars, setting in train the global Gold Standard run from London until the start of World War I.
Enough ancient history; fast forward to today, and the UK’s real rate of interest is now the worst since 1975, back when inflation was running well into double digits but at least the central bank made a pretence of addressing it, setting a nominal base rate of 11%. Last month’s inflation reading was only a 20-year high, but all-time record-low interest rates make cash such a losing proposition, savers are actively paying to hold cash in the bank. And these unsecured creditors are lending to institutions whose “underlying problem is one of solvency not liquidity” as Bank of England governor Mervyn King himself put it in a speech this week.
Losing real value by holding money with insolvent banks sounds like financial suicide. Which for today’s moneyed classes – those millions of savers, pensioners and would-be retirees raised by the welfare state – should sound uncomfortably like the “euthanasia of the rentier” hoped for in the mid-1930s by J.M.Keynes, apostle of deficit spending (and nemesis of the Gold Standard), and slowly put into practice after World War Two by decades of sub-zero real interest rates. Taxation of unearned income peaking at 98% sure helped, too.
“Interest today rewards no genuine sacrifice, any more than does the rent of land,” wrote Keynes in 1936, just ahead of that “depression within a depression” which forced economists to coin a new term, “recession”.
“The owner of capital can obtain interest because capital is scarce,” Keynes went on, “just as the owner of land can obtain rent because land is scarce. But whilst there may be intrinsic reasons for the scarcity of land, there are no intrinsic reasons for the scarcity of capital…I see, therefore, the rentier aspect of capitalism as a transitional phase which will disappear when it has done its work…The euthanasia of the rentier, of the functionless investor, will be nothing sudden, merely a gradual but prolonged continuance of what we have seen recently in Great Britain, and will need no revolution.”
Today’s savers might not see themselves as “functionless investors” anymore than they see themselves as stuffed-shirt aristocrats wielding “the cumulative oppressive power of the capitalist to exploit the scarcity-value of capital”. But the owner of capital, however modest, can no longer obtain interest, that much is plain. Because capital is no longer scarce. Solvency is. And there’s a whole heap of 21st-century rentiers waiting to put out of their misery yet.
Looking to Buy Gold today…?
Suicide of the Saver
by Adrian Ash
BullionVault
Wednesday, 19 October 2011
Savers and pensioners! Your murderers need no revolution to storm your stately homes and
palaces…
IT’S NOW 100 years since Great Britain established its welfare state. Shortly after, and as
the First World War kicked off, it abandoned the free exchange of bullion for notes under the
classical Gold Standard.
Those 3 events were far from unrelated, but 100 years later it’s the monetary shift which
feels most pressing right now. Yes, political fighting over the welfare state is hotting up,
but a European shooting match looks unlikely (for the time being). Whereas UK savers and
retirees, like their peers across the continent, in North America and pretty much everywhere
else, are getting slaughtered.
Compared to the previous 100 years, real UK interest rates – the returns paid to cash deposits
over and above inflation – have been atrocious since 1911. Averaging less than 0.9% per
year, they’ve been a fraction of the 4.4% averaged in the 100 years starting in 1811, just after
the British Parliament’s Bullion Committee recommended a full return to gold following the
Napoleonic Wars, setting in train the global Gold Standard run from London until the start of
World War I.
Enough ancient history; fast forward to today, and the UK’s real rate of interest is now the
worst since 1975, back when inflation was running well into double digits but at least the
central bank made a pretence of addressing it, setting a nominal base rate of 11%. Last
month’s inflation reading was only a 20-year high, but all-time record-low interest rates make
cash such a losing proposition, savers are actively paying to hold cash in the bank. And these
unsecured creditors are lending to institutions whose “underlying problem is one of solvency
not liquidity” as Bank of England governor Mervyn King himself put it in a speech last night.
Losing real value by holding money with insolvent banks sounds like financial suicide.
Which for today’s moneyed classes – those millions of savers, pensioners and would-be
retirees raised by the welfare state – should sound uncomfortably like the “euthanasia of the
rentier” hoped for in the mid-1930s by J.M.Keynes, apostle of deficit spending (and nemesis
of the Gold Standard), and slowly put into practice after World War Two by decades of sub-
zero real interest rates. Taxation of unearned income peaking at 98% sure helped, too.
“Interest today rewards no genuine sacrifice, any more than does the rent of land,” wrote
Keynes in 1936, just ahead of that “depression within a depression” which forced economists
to coin a new term, “recession”.
“The owner of capital can obtain interest because capital is scarce,” Keynes went on, “just
as the owner of land can obtain rent because land is scarce. But whilst there may be intrinsic
reasons for the scarcity of land, there are no intrinsic reasons for the scarcity of capital…I see,
therefore, the rentier aspect of capitalism as a transitional phase which will disappear when it
has done its work…The euthanasia of the rentier, of the functionless investor, will be nothing
sudden, merely a gradual but prolonged continuance of what we have seen recently in Great
Britain, and will need no revolution.”
Today’s savers might not see themselves as “functionless investors” anymore than they see
themselves as stuffed-shirt aristocrats wielding “the cumulative oppressive power of the
capitalist to exploit the scarcity-value of capital”. But the owner of capital, however modest,
can no longer obtain interest, that much is plain. Because capital is no longer scarce. But
solvency is.
Adrian Ash
BullionVault



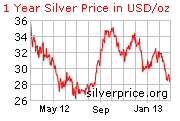
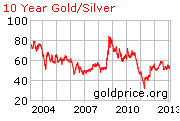
Government admission of price suppression: Report by South Carolina State Treasurer’s Office
-
[Active updates: Developing stories] The South Carolina Treasurer’s Office, acting upon a directive from the state legislature, has recently published a report on the advisability of investing in gold and silver. Basically, the state legislature wanted to know if it’s wise to invest public funds under it’s custody in gold & silver.
Here’s what the Treasurer’s Office has to say about itself:
This is a tall order, hence we can assume that the report must be well researched and credible. It concluded that it is not advisable to invest public funds in gold & silver because:-
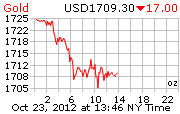
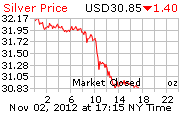
While the timestamp of the document was 27 Feb 2012, it can be assumed that the report was prepared soon after the end of September 23, 2011 due to this inclusion. From the perspective of a short term investment, that was a pretty good call, considering the fact that gold and silver have been taken down to $1624 and $31.40 respectively as I write.
However, this piece is not about how good the Treasurer’s Office was at making an investment call based on price. Neither is it about whether gold & silver is in a bubble. These conclusions (2) & (3) are opinions of the Treasurer’s Office, which are subjective. Of greater interest are the facts revealed in the body of the report.
Regular readers of this blog would have noticed that there are several key issues that are repeatedly discussed or highlighted here (through news feeds or third party contributions). They include:-
Items (1) to (4) are often disputed by the mainstream media and investors, sometimes referring to them as conspiracy theories. Hence, it is most interesting to see what this government published report has to say about these 6 issues.
Price Suppression is Real
In one short paragraph, this report confirms in no uncertain terms the truth behind the so called “conspiracy theories”. Not only does it confirm the existence of price suppression, it discloses the WHOs and the HOWs!
Risks of holding gold through ETFs, Certificates, Bank Accounts & other Derivatives
It has been repeatedly emphasized here that the only secure means of owning gold & silver is by holding physical coins and bars in your own possession or stored in a private vault outside the banking system. Anything else is a derivative - a paper or electronic representation of the real thing.
This report explains the nature of these derivatives and lists the risks associated with each, together with reasons why the Treasury’s Office advised against investing in them.
The full report in pdf is available for download at the South Carolina Treasurer’s website. Text from relevant sections is reproduced below with comments related to the 6 items above highlighted. Most of the remarks are self explanatory. There are, however, two groups of comments that warrant some discussion.
1. Allocated & Unallocated Accounts
The above describes two products offered by banks to clients who want to invest in gold (or silver) without having to deal with the physical metals. For example, when a bank accepts $2,000 from a customer and issues a gold certificate or credits the customer’s gold account under the unallocated system, the bank is not obliged to buy and store 1.2 oz (at current price) of gold on behalf of the customer. It holds only a tiny portion of that amount in gold. Hence when many of its the customers decide to redeem their certificates at the same time, the bank will not have sufficient gold to deliver. This is what’s referred to as a “run on the bank’s gold on deposit”. The same applies when depositing cash in your bank. The practice of keeping only a tiny fraction of what’s rightfully belonging to the customers (gold or cash) is referred to as fractional reserve banking.
When selling allocated gold products, the bank is legally required to hold 100% of the customers deposit in physical metal. For example, if a customer deposits sufficient cash to own a 400 oz gold bar and is assigned a bar bearing serial No: AGR Matthey 156571, how can one be sure that the same bar or a portion thereof is not assigned to another customer at the same time? That’s the issue raised by the report - and the risk is real.
This brings us back to “the only secure means of owning gold & silver is by holding physical coins and bars in your own possession or stored in a private vault outside the banking system”. If you have to use a third party to store your metals, use specialized private vaults instead, because banks operate on a fractional reserve banking system.
There are many companies outside the banking system that offer secure vaulting services. Generally, they have very high transparency, including publishing audited client holdings on the web for public scrutiny (without any login required). Of course clients’ ID are anonymous, and known only to the operator and the client.
Try these links:
GoldMoney bar list and BullionVault client holdings. Their reviews can be found here.
Learn more about private vaulting services, including issues like ownership, custody, bailment, counter-party risks, and performance risks.
2. Reason for not investing in physical gold & silver
The report listed 5 ways to invest in gold & silver - ETPs, Certificates, Accounts, Derivatives and physical coins & bars. Notice how it highlights & explains all the risks associated with ETPs, Certificates, Accounts and Derivatives and the reasons why it is not advisable for the Treasury to invest in these.
Notice also that there are NO risk associated with physical metals. The only reason given for not investing in coins and bars is “South Carolina does not have the capacity to store or funding to secure gold and silver bullion”.
What a lame excuse! Do they not know that in April last year, “The University of Texas Investment Management Co., the second-largest U.S. academic endowment, took delivery of almost $1 billion in gold bullion“?
-
Proviso 89.145 GP:
Gold & Silver Investments
Office of State Treasurer
-
GOLD AND SILVER AS AN INVESTMENT:
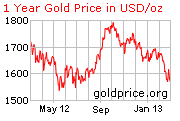
Historically, investors have purchased gold as a hedge against an economic, a political, or a currency crisis. A decline in investment markets, a growing national debt, a weak currency, increasing inflation, military conflicts and social unrest are the most common reasons for investment in gold. Currently, gold and silver are at historic highs leading many expert investors to conclude that a bubble has been created in the precious metals market. Since the US recession began, the value of gold and silver has increased as investment markets perform poorly, troublesome economic news is announced, and when uncertainty in international markets intensifies.
Similar to other commodities, the value of gold and silver is determined by supply and demand, as well as speculation. The Federal Reserve, The London Bullion Market Association, JP Morgan Chase, and HSBC Holdings have practiced fractional-reserve banking and engaged in naked short selling causing artiñcial price suppression.
There are several ways to invest in gold and silver: bars, coins, ETP’s, certificates, accounts, and derivatives. If a state were to choose to invest in gold (and silver), it would likely choose to invest by:
1. ETP’s-Exchange Traded Products. This allows the stakeholder to invest in bullion without having to store bars and coins. The ñrst gold ETF (Exchange Traded Fund) was created in 2003 and has been viewed largely as a success, but has also been compared to investing in mortgagebacked securities. The annual expenses of the fund (storage, insurance, and management fees) are charged by selling a small amount of gold represented by each certificate, so the amount of gold in each certificate will gradually decline over time. ETF’s are investment companies that are legally classified as open-end companies or Unit Investment Trusts (UIT), but differ from traditional open-end companies and U]T’s. The main differences are that ETF’s do not sell directly to investors and they issue their shares in what are called Creation Units. Also, the Creation Units may not be purchased with cash but a basket of securities that mirrors the ETF‘s portfolio. The Usually, the Creation Units are split up and re-sold on a secondary market.
2. Certificates- allow investors to avoid the risks and costs associated with the transfer and storage of bullion by taking on a set of risks and costs associated with the certificate itself. Banks may issue gold certificates for gold which is allocated (non-fungible) or unallocated (fungible). Unallocated gold certiñcates are a form of fractional reserve banking and do not guarantee an equal exchange for metal in the event of a run on the bank’s gold on deposit. Allocated gold certificates should be correlated with speciñc numbered bars, however it is difficult to prove whether a bank is improperly allocating a single bar to more than one investor. The US ñrst authorized the use of gold certificates in 1863. By the early l930’s the US placed restrictions on private gold ownership and therefore, the gold certificates stopped circulating as money, but certificates are still issued by gold pool programs for investment purposes.
3. Accounts- Many banks offer gold accounts where gold can be instantly bought or sold just like any foreign currency on a fractional reserve (non-allocated, fungible) basis. Pool accounts, facilitate highly liquid, but unallocated claims on gold owned by the company. Digital gold currency systems operate like pool accounts and additionally allow the direct transfer of fungible gold between members of the service. Different accounts impose varying types of intermediation between the client and their gold. One of the most important differences between accounts is whether the gold is held on an allocated or unallocated basis. Another major difference is the strength of the account holder’s claim on the gold, in the event that the account administrator faces gold-denominated liabilities, asset forfeiture, or bankruptcy.
4. Derivatives- The product symbol for gold futures is GC, and it is traded in a standard contract
size of 100 troy ounces. In the US, gold futures are primarily traded on the New York Commodities Exchange (COMEX). As of 2009 holders of COMEX gold futures have experienced problems taking delivery of their metal. Along with chronic delivery delays, some investors have received delivery of bars not matching their contract in serial number and weight. Because of these problems, there are concerns that COMEX may not have the gold inventory to back its existing warehouse receipts.
ADVISABILITY:
There is no statute preventing the State from investing in gold and silver. The various methods of investment in gold and silver each carry different and often significant risks, the foremost being speculation. As the US has experienced the recent bursts in the housing and tech bubbles, it is important to take caution when contemplating an unconventional investment. Taxpayer money (state funds and state pension) across the US has not typically been used to invest in gold or silver bullion.
Recently, with the uncertainty in global markets, the devaluation of the dollar, rising inflation, and a flat US economy, there has been a renewed interest in either moving back to a gold standard, investing in gold or both. The value of gold and silver has significantly increased in the last decade, meaning it would cost a great deal to invest at this time.
Risks:
1. Bars and coins- South Carolina does not have the capacity to store or funding to secure gold and silver bullion. For these reasons the State Treasurer’s Office does not advise investing in gold and silver bars and coins.
2. ETP’s- The armual expenses and costs associated with this type of investment are high. In recent years there have been issues surrounding gold ETP’s. The purchase price provides the investor with a fluctuating amount (in weight) of the metal. Over time, as value increases and more investors participate in the fund, the amount of metal owner by the investor decreases. ETP’s can also be split and sold on the secondary market. For these reasons the State Treasurer’s Ofñce does not advise investing in ETP’s for gold and silver.
3. Certificates- Certificates for allocated gold present an accountability problem. Allocated gold certificates are supposed to be correlated with speciñc numbered bars; however, it is difficult to verify whether a bank is improperly allocating a single bar to more than one investor. Also, unallocated gold certificates are a form of fractional reserve banking and do not guarantee an equal exchange for metal in the event of a run on the bank’s gold on deposit. This is in conflict with S.C. Code of Laws 1976 SECTION 11-9-660. For these reasons, the State Treasurer’s Office cannot advise investing in gold and silver certificates.
4. Accounts- Similar to the risks associated with gold and silver certificates, allocated and unallocated metals held in accounts produce similar accountability problems. The strength of the account holder’s claim on metals is subject to the account administrators liabilities, assets, and/or solvency. Per S.C. Code of Laws 1976 SECTION 11-9-660, the State Treasurer’s Office cannot advise investing in gold and silver accounts.
5. Derivatives- Over the last three years, gold futures traded on the New York Commodities Exchange (COMEX) have encountered significant accountability problems. Holders of COMEX gold ñltures have frequently experienced delivery delays of their metals. Once delivered, there have been many reports of inaccurate weights and serial numbers on bars that do not match the holder’s contract. For these reasons the State Treasurer’s Office does not advise investing in gold and silver derivatives.
-
Gold: April 2012
-
Having read the above, it may now be easier to make sense of the sharp price decline for both gold & silver over the past 2 days. Lets now ask some questions. Was the price action due to:
The mainstream media attributed this week’s sharp price decline to improving economy, low inflation and no imminent QE announcements following the release of the latest FOMC meeting minutes. Given that the above statement was published just 5 weeks before the FOMC minutes, who is lying?
-
Developing Stories
12 Apr:
Jason Hommel explains what Blythe Masters actually meant by “the underlying client position that we’re hedging”.
11 Apr:
Ted Butler, the pioneer of silver manipulation investigation finally broke his silence over the Blythe Masters denial video clip. By far, this is THE best, most level-headed, objective rebuttal to Masters’ famous words that they are “not running a large directional position”. Read “JPM’s TV appearance” posted at Silverseek.com.
10 Apr:
-
7 Apr:
Mike Maloney on RT discussing gold & silver manipulation, Blythe Masters denial of JPM’s role in price manipulation, “First government admission of price suppression” & High Frequency Sheering. Must Watch!
-
6 Apr:
Further Reading:
-
Share this:
Like this: