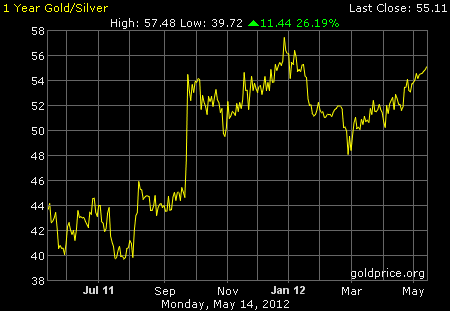
The Economist’s Perfectly Useless Gold
On the Letters’ page of The Economist last week, Nils Sandberg from Cambridge University’s Judge Business School presented a common argument against gold’s current value.
SIR – Buttonwood discussed the possibility of gold as a bubble (April 30th). Of course it is—it has almost no real value and, as you say, no revenue or cashflow. It is an iconic commodity both emotionally as jewellery and intellectually as a stable investment, and has long been a guiding point for commodity inflation. But what gives it that place?
Gold has few uses beyond jewellery, and yet the trading of gold internationally is many times larger than that industry. Today it, like a share with no dividends, is a purely speculative investment and its value is entirely a function of such speculation. A high gold price does not cripple an industry or a nation; the current owners just get richer. A currency with a constant influx, the rise in value of gold is like a great Ponzi scheme where the future must always pay today’s bills.
Commodities with stable consumption and high volume production (like wheat and iron) are better indicators of real prices and as they continue to rise inflation is a risk. Gold is different. One day the money will dry up, and the house of cards will fold.
Nils Sandberg
Judge Business School
Cambridge
-
Here’s founder & CEO of BullionVault, Paul Tustain’s response.
Tuesday, 31 May 2011
Would you – or China – rather own gold 8 years from now, or US Treasury bonds…?
According to him, gold is in bubble territory because it has few industrial uses. Disproving Mr Sandberg’s thesis is childishly simple.
- Take one $20 bill out of your wallet;
- Consider the industrial applications of the paper it is printed on;
- Now burn it.
Well, why didn’t you? After all, its value – according to Mr Sandberg’s thesis – rests on the paper’s usefulness in industrial processes.
Nevertheless it’s still interesting to understand why gold (like $20 bills) is valued above its manufacturing relevance. Unsurprisingly the answer lies in marginal utility.
Gold offers humanity one exceptionally useful property; it has an extraordinarily stable stock. There are 166,000 tonnes of the stuff above ground (worth about $8 trillion) of which about 88% is held as a value store of sorts, in jewelry (52%) and bullion (36%). The stock is growing by about 1.5% a year, from the combined efforts of all the world’s miners.
It is because gold is each of (i) geologically rare, (ii) elemental (i.e. incapable of being manufactured) and (iii) industrially useless, that it has this reliable stock quantity. Nothing else can do it; not silver, which is 80 times more common in the ground, nor platinum, which is far too useful as a catalyst to offer stock stability.
Reliable scarcity is the key property savers require of money, which otherwise fails to store value. But of course we don’t need gold to deliver reliable scarcity, we can usually create that reliable scarcity artificially, as we do with our modern currencies.
Now the marginal utility explanation. When new currency is too freely issued reliable scarcity becomes under-supplied, and savers go in search of it. Having seen artificial reliable scarcity fail in one currency, the promise of it in another is unconvincing, so they turn to natural reliable scarcity, and demand for it increases dramatically as governments print money. This is what drives gold up.
Mr Sandberg is right though, that gold will eventually go down again, when currencies’ artificial scarcity once more becomes reliable, and when those currencies start to generate a yield. But in the meantime it looks irrationally optimistic to hope that the US government – faced with a $21 trillion debt – will not print more and more money.
The question, therefore, is whether the savers who own $100 trillion of dated debt instruments in the bond markets will take fright at continuing money printing policies of the US and other governments. That $100 trillion of dated debt has already started running down the clock. It is shifting to the short end, where it behaves more and more like cash. Maybe its holders will demand cash (as is their right) at its redemption. The sums involved would swamp the $15 trillion of cash and near-term deposit instruments currently in issue.
People who choose to buy gold are increasingly aware of this possibility. We don’t know whether the Dollar, the Euro, the Yen and the Pound (all of which have started a debt market drift to the short end) will ultimately go into the currency death spiral. We are just mindful that it is the usual destiny of currencies driven by political expedience toward the printing press. It looks like a possibility at least.
To finish with here’s the brainteaser which the Chinese are currently wrestling with. Now that you know the US debt profile is slowly shifting to the short end, and represents about six times the currency in issue, you are required to choose today something to own in 2020. What would you (or China) rather have – a tenth of the US Treasury’s paper bond debts, or five times its very large gold reserve?
At current market prices these two are worth about the same. But in the intervening 8 years, the US government has budgeted to issue $8 trillion net of its own bonds, representing an increase in the stock of 57%. A further $1 trillion of gold will be mined worldwide, an increase in the global stock of 12%.
Paul Tustain
BullionVault
-
… But
who has been, and will be buying up all these debt?
FED Monetary Base as at May 18, 2011
-
and while they’re printing all these money, they might as well print more food stamps.
Maybe that’s why they say gold is useless. Who needs gold when you’re living out
The American Dream - Free Money, Free Food, Cheap Housing!
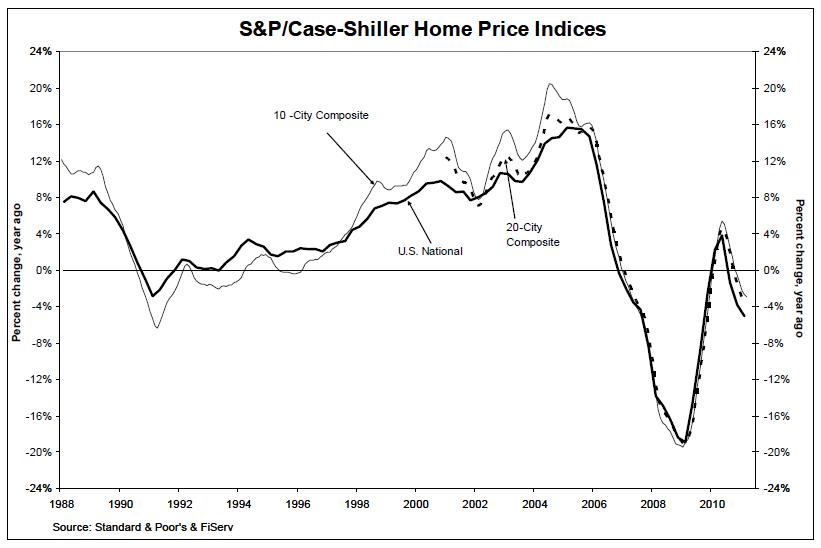
“Double dip” declared as U.S. housing prices tumble
-


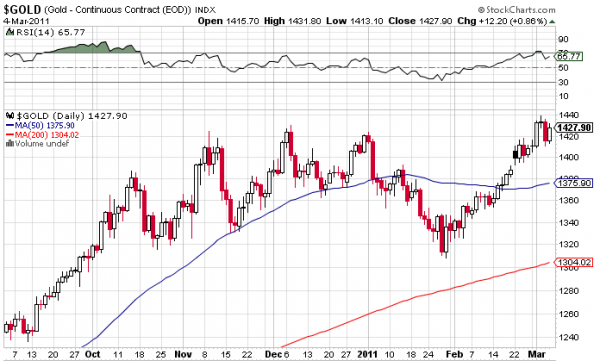
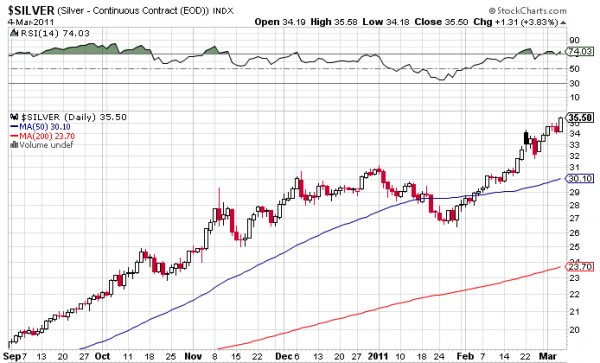

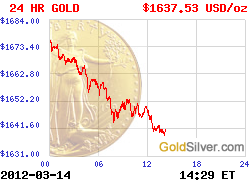
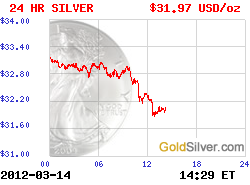
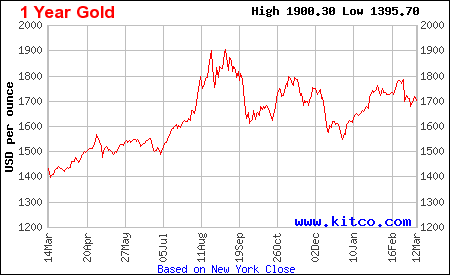 More Charts: 1-Month, 1-Year, 5-Year, 10-Year
More Charts: 1-Month, 1-Year, 5-Year, 10-Year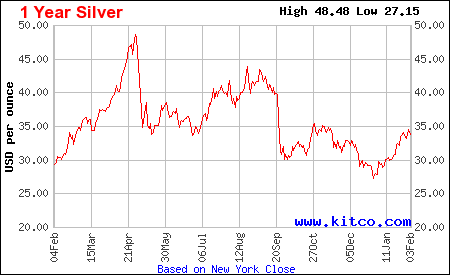 More Charts: 1-Month, 1-Year, 5-Year, 10-Year
More Charts: 1-Month, 1-Year, 5-Year, 10-Year