Trading Of Over The Counter Gold And Silver To Be Illegal Beginning July 15
Tyler Durden | Zero Hedge | June 19, 2011
One small step toward Executive Order 6102 part 2, and one giant leap for corruptcongressmankind.
From: FOREX.com <[email protected]>
Date: Fri, Jun 17, 2011 at 6:11 PM
Subject: Important Account Notice Re: Metals Trading
To: xxxImportant Account Notice Re: Metals Trading
We wanted to make you aware of some upcoming changes to FOREX.com’s product offering. As a result of the Dodd-Frank Act enacted by US Congress, a new regulation prohibiting US residents from trading over the counter precious metals, including gold and silver, will go into effect on Friday, July 15, 2011.
In conjunction with this new regulation, FOREX.com must discontinue metals trading for US residents on Friday, July 15, 2011 at the close of trading at 5pm ET. As a result, all open metals positions must be closed by July 15, 2011 at 5pm ET.
We encourage you to wind down your trading activity in these products over the next month in anticipation of the new rule, as any open XAU or XAG positions that remain open prior to July 15, 2011 at approximately 5:00 pm ET will be automatically liquidated.
We sincerely regret any inconvenience complying with the new U.S. regulation may cause you. Should you have any questions, please feel free to contact our customer service team.
Sincerely,
The Team at FOREX.com
So far we have only received this warning from Forex.com. We are waiting to see which other dealers inform their customers that trading gold and silver over the counter will soon be illegal.
It appears that Forex.com’s interpretation of the law stems primarily from Section 742(a) of theDodd-Frank act which “prohibits any person [which again includes companies]from entering into, or offering to enter into, a transaction in any commodity with a person that is not an eligible contract participant or an eligible commercial entity, on a leveraged or margined basis.”
Some prehistory from Hedge Fund Law Blog:
The Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act (“Act”) has changed a number of laws in all of the securities acts including the Commodity Exchange Act. Two specific changes deal with certain transactions in commodities on the spot market. Specifically, Section 742 of the Act deals with retail commodity transactions. In this section, the text of the Commodity Exchange Act is amended to include new Section 2(c)(2)(D) (dealing with retail commodity transactions) and new Section 2(c)(2)(E) (prohibiting trading in spot forex with retail investors unless the trader is subject to regulations by a Federal regulatory agency, i.e. CFTC, SEC, etc.). According to a congressional rulemaking spreadsheet, these are effective 180 days from the date of enactment.
We provide an overview of the new sections and have reprinted them in full below.
New CEA Section 2(c)(2)(D) – Concerning Spot Commodities (Metals)
The central import of new CEA Section 2(c)(2)(D) is to broaden the CFTC’s power with respect to retail commodity transactions. Essentially any spot commodities transaction (i.e. spot metals) will be subject to CFTC jurisdiction and rulemaking authority. There is an exemption for commodities which are actually delivered within 28 days. While the CFTC wanted an exemption in which commodities would need to be delivered within 2 days, various coin collectors were able to lobby congress for a longer delivery period (see here).
It is likely we will see the CFTC propose regulations under this new section and we will keep you updated on any regulatory pronouncements with respect to this new section.
New CEA Section 2(c)(2)(E) – Concerning Spot Forex
The central import of new CEA Section 2(c)(2)(E) is to regulate the spot forex markets. While the section requires the CFTC to finalize regulations with respect to spot forex (which were proposed earlier in January), it also, interestingly, provides oversight of the markets to other federal regulatory agencies such as the CFTC. This means that in the future, different market participants may be subject to different regulatory regimes with respect to trading in same underlying instruments. A Wall Street Journal article discusses the impact of this with respect to firms which engage in other activities in addition to retail forex transactions. The CFTC’s proposed rules establish certain compliance parameters for retail forex transactions, requires registration of retail forex managers and requires such managers to pass a new regulatory exam called the Series 34 exam. We do not yet know whether the other regulatory agencies will adopt rules similar to the CFTC or if they will write rules from scratch.
Next, from Henderson & Lyman:
The prohibition of Section 742(a) does not apply, however, if such a transaction results in actual delivery within 28 days, or creates an enforceable obligation to deliver between a seller and a buyer that have the ability to deliver, and accept delivery of, the commodity in connection with their lines of business. This may be problematic as in most spot metals trading virtually all contracts fail to meet these requirements. As a result, although the courts’ interpretation of Section 742(a) is unknown, Section 742(a) is likely to have a significantly negative impact on the OTC cash precious metals industry. Here too, it is essential that those who offer to be a counterparty to OTC metals transactions seek professional help to discuss possible operational and regulatory contingency plans.
The actual rule language exempts a transaction if it “results in actual delivery within 28 days or such other period as the Commission may determine by rule or regulation based upon the longer period as the Commission may determine by rule or regulation based upon the typical commercial practice in cash or spot markets for the commodity involved;” Alas, the commission has decided not to intervene and keep the exemption status window so small as to affect virtually all exchanges which transact in the gold and silver spot market.
Elimination of OTC Forex
Effective 90 days from its inception, the Dodd-Frank Act bans most retail OTC forex transactions. Section 742(c) of the Act states as follows:
…A person [which includes companies] shall not offer to, or enter into with, a person that is not an eligible contract participant, any agreement, contract, or transaction in foreign currency except pursuant to a rule or regulation of a Federal regulatory agency allowing the agreement, contract, or transaction under such terms and conditions as the Federal regulatory agency shall prescribe…
This provision will not come into effect, however, if the CFTC or another eligible federal body issues guidelines relating to the regulation of foreign currency within 90 days of its enactment. Registrants and the public are currently being encouraged by the CFTC to provide insight into how the Act should be enforced. See CFTC Rulemakings regarding OTC Derivatives located at the following website address, under Section XX – Foreign Currency (Retail Off Exchange). It is essential that OTC forex participants seek professional help to discuss possible operational and regulatory contingency plans.
Elimination of OTC Metals
As for OTC precious metals such as gold or silver, Section 742(a) of the Act prohibits any person [which again includes companies]from entering into, or offering to enter into, a transaction in any commodity with a person that is not an eligible contract participant or an eligible commercial entity, on a leveraged or margined basis. This provision intends to expand the narrow so called “Zelener fix” in the Farm Bill previously ratified by congress in 2008. The Farm Bill empowered the CFTC to pursue anti-fraud actions involving rolling spot transactions and/or other leveraged forex transactions without the need to prove that they are futures contracts. The Dodd-Frank Act now expands this authority to include virtually all retail cash commodity market products that involve leverage or margin – in other words OTC precious metals.
The prohibition of Section 742(a) does not apply, however, if such a transaction results in actual delivery within 28 days, or creates an enforceable obligation to deliver between a seller and a buyer that have the ability to deliver, and accept delivery of, the commodity in connection with their lines of business. This may be problematic as in most spot metals trading virtually all contracts fail to meet these requirements. As a result, although the courts’ interpretation of Section 742(a) is unknown, Section 742(a) is likely to have a significantly negative impact on the OTC cash precious metals industry. Here too, it is essential that those who offer to be a counterparty to OTC metals transactions seek professional help to discuss possible operational and regulatory contingency plans.
Small Pool Exemption Eliminated
Pursuant to Section 403 of Act, the “privateadviser” exemption, namelySection 203(b)(3) of the Investment Advisers Act of 1940 (“Advisers Act”), will be eliminated within one year of the Act’s effective date (July 21, 2011). Historically, many unregistered U.S. fund managers had relied on this exemption to avoid registration where they:
(1) had fewer than 15 clients in the past 12 months;
(2) do not hold themselves out generally to the public as investment advisers; and
(3) do not act as investment advisers to a registered investment company or business development company.
At present, advisers can treat the unregistered funds that they advise, rather than the investors in those funds, as their clients for purposes of this exemption. A common practice has thus evolved whereby certain advisers manage up to 14 unregistered funds without having to register under the Advisers Act. Accordingly, the removal of this exemption represents a significant shift in the regulatory landscape, as this practice will no longer be allowable in approximately one year.
Also an important consideration, the Dodd-Frank Act mandates new federal registration and regulation thresholds based on the amount of assets a manager has under management (“AUM”). Although not yet underway, it is possible that various states may enact legislation designed to create a similar registration framework for managers whose AUM fall beneath the new federal levels.
Accredited Investor Qualifications
Section 413(a) of the Act alters the financial qualifications of who can be considered an accredited investor, and thus a qualified as eligible participant (“QEP”). Specifically, the revised accredited investor standard includes only the following types of individuals:
1) A natural person whose individual net worth, or joint net worth with spouse, is at least $1,000,000, excluding the value of such investor’s primary residence;
2) A natural person who had individual income in excess of $200,000 in each of the two most recent years or joint income with spouse in excess of $300,000 in each of those years and a reasonable expectation of reaching the same income level in the current year; or
3) A director, executive officer, or general partner of the issuer of the securities being offered or sold, or a director, executive officer, or general partner of a general partner of that issuer.
Based on this language, it is important to note that the revised accredited investor standard only applies to new investors and does not cover existing investors. However, additional subscriptions from existing investors are generally treated as requiring confirmation of continuing investor eligibility.
On July 27th, 2010, the SEC provided additional clarity regarding the valuation of an individual’s primary residence when calculating net worth. In particular, the SEC has interpreted this provision as follows:
Section 413(a) of the Dodd-Frank Act does not define the term “value,” nor does it address the treatment of mortgage and other indebtedness secured by the residence for purposes of the net worth calculation…Pending implementation of the changes to the Commission’s rules required by the Act, the related amount of indebtedness secured by the primary residence up to its fair market value may also be excluded. Indebtedness secured by the residence in excess of the value of the home should be considered a liability and deducted from the investor’s net worth.
h/t Ryan


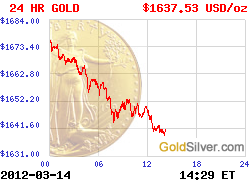
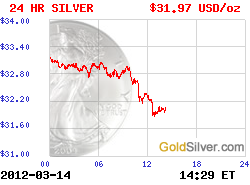
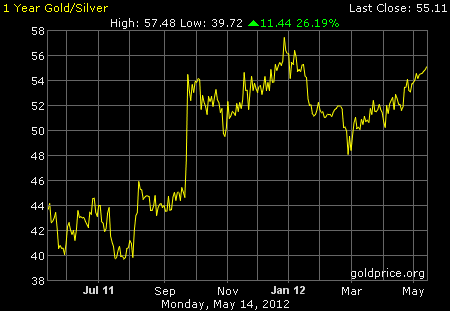
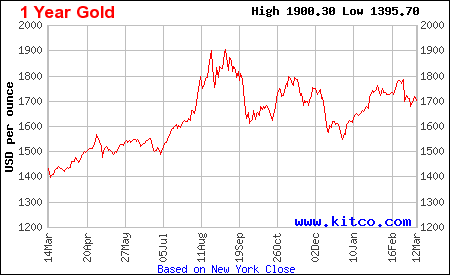 More Charts: 1-Month, 1-Year, 5-Year, 10-Year
More Charts: 1-Month, 1-Year, 5-Year, 10-Year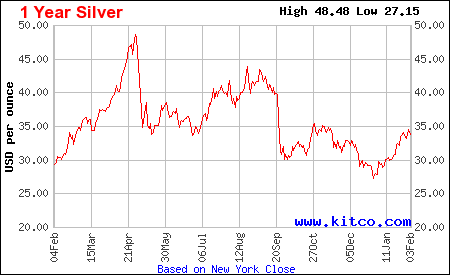 More Charts: 1-Month, 1-Year, 5-Year, 10-Year
More Charts: 1-Month, 1-Year, 5-Year, 10-Year